Learn the step-by-step commands to install Apache Web servers on Linux such as Debian, Ubuntu, RedHat, CentOS, Almalinux, Rocky, Linux Mint, OpenSUSE, Amazon Linux, and more…
Web servers are an important part of the Internet, but also provide useful services even for local networks. Configuring a web server with Apache is not a difficult task, yet, here we learn how to do that…
However, before moving further let’s know a little bit about the Apache web server.
What is the function of a Web Server?
The key usage of the web servers is to deliver HTML and image content via HTTP or HTTPS protocols. Whenever we enter some web address in our browser to open some website or an HTML page, the browser requests for that to web server on port 80 (“http://”) or port 443 (“https://”), if the page is present there the same will be displayed to you. Well, web servers and browsers are key technologies of the Internet. Both provide an infrastructure to retrieve information, store data, shop online, and communicate on social networks.
In terms of browsers, we have popular Chrome, FireFox, Edge, Brave, Tor and etc. When it comes to Web server software platforms, similarly we have many popular names such as IIS, Apache, LightSpeed, Nginx, and more. However, the Apache HTTP server is one of the most widely used web servers. It has been around for over 20 years and many example configurations refer to Apache. Although many web application users prefer Nginx over Apache because of its less consumption of PC resources and ability to serve huge number of users. While others prefer to use both, Apache as a web server along with Nginx as a reverse proxy. The advantage of this is that the load can be distributed between the two servers and the overall performance can be increased. NGINX vs. Apache: Comparision of web servers to host your website
Well, Apache web server, most of the time installed with other tools because in today’s world mainly we will not use simple, static HTML files on a web server, but will use a CMS or other web application. Such as WordPress, Joomla Nextcloud, and more to create dynamic websites. And for this, the web server needs script languages usually PHP, Perl, or Python. Basically, the web server can start any external programs regardless of the programming language used, whose HTML or text output it forwards to the client (browser).
Learn how to install WordPress on Ubuntu Linux.
Steps to install Apache web server on Linux
The given commands here can be followed on most Linux regardless of their versions.
On Ubuntu and Debian Linux
The commands shown in this tutorial will work on all Debian and Ubuntu-based systems such as Elementary, Linux Mint, MX Linux, POP OS, and more to install the Apache web server
Step 1: Log in to Linux Server
First access the command terminal of your Linux server where you want to install the Apache webserver. Those who are using a cloud or remote server can use SSH to remotely log in.
Step 2: Run system update
The second step is to run the system update command that will install all the available updates on your system. It will also refresh the APT package manager’s cache.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Step 3: Install Apache on Linux
Next, use the APT package manager and install the Apache web server on your Linux. The best thing we don’t need any third-party repository to install it. All the packages are available using the Linux default system repository.
sudo apt install apache2
Step 4: Enable and check service
Although the service of the Apache web server will automatically be set by the system to start with the boot, yet, let’s run the given command to confirm the same:
sudo systemctl enable --now apache2
To check whether the service is running absolutely fine or not, run:
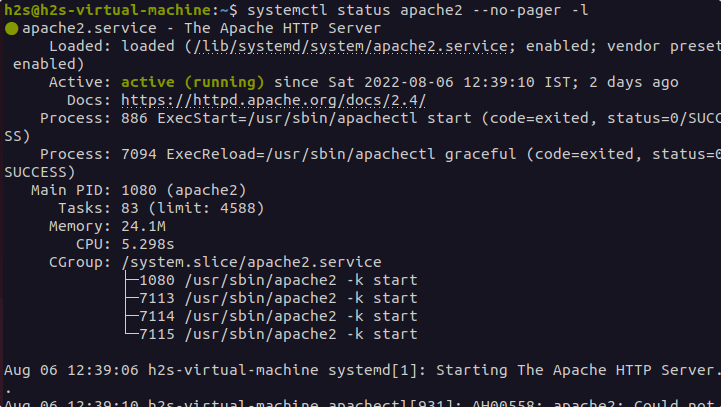
systemctl status apache2 --no-pager -l
Output:
On RedHat, Fedora, Amalinux, Rocky, CentOS, Oracle, Amazon Linux
Well, although Ubuntu and Debian are also Linux but the command to install the Apache web server on RHEL-based Linux will be different. Hence, if your Linux is based on RedHat then here are the commands to follow:
Step 1: Access Terminal
The very first thing we want to access is the command line. Hence, either direct access the server terminal or use the SSH remotely.
Step 2: Update Linux
Just like we did for Ubuntu, we also first run the system update command for RHEL-based Linux systems as well. Here is the one to follow:
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf upgrade
Step 3: Install Httpd or Apache on Linux
In the Redhat-based Linux, the Apache is known as HTTPD, hence here we will use the DNF package manager of the RHEL systems to install the web server.
sudo dnf install httpd
Step 4: Start and Check the status
To enable, start and check the status of the Apache web server service after the installation, run the given commands:
sudo systemctl enable --now httpd
To check status:
systemctl status httpd --no-pager -l
Command to stop and restart Apache
Well, if you want to stop, reload and restart the Apache web server in the future then for that here are the commands to use:
To reload
On Ubuntu & Debian systems:
sudo systemctl reload apache2
On Redhat-based systems:
sudo systemctl reload httpd
To restart
On Ubuntu & Debian systems:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
On Redhat-based systems:
sudo systemctl restart httpd
To Stop
On Ubuntu & Debian systems:
sudo systemctl stop apache2
On Redhat-based systems:
sudo systemctl stop httpd
Uninstall or Remove completely
If you have performed some wrong configuration or do not want the Apache web server anymore on your Linux system then here are the commands to completely remove it.
For Ubuntu and Debian-based systems:
sudo apt autoremove --purge apache2
For Redhat-based systems:
sudo dnf remove httpd
Other Articles:
⇒ How to install Apache on Almalinux 8 / Rocky Linux 8
⇒ How to Install WordPress on AlmaLinux 8
⇒ Install NextCloud server on AlmaLinux 8
⇒ Set Up Nginx as a Reverse Proxy For for Apache on Ubuntu
⇒ How to Install phpMyAdmin with Apache on Ubuntu Linux